'''Speedy Internet Connection with MikroTik RB750 , RB750G , RB750GL ''
Speedy Internet Connection with MikroTik RB750 , RB750G , RB750GL
MikroTik
RouterBoard RB750 is the latest generation Mikrotik routerboard output
is very small and designed for SOHO use. Has 5 Ethernet ports 10/100,
with the new Atheros 400MHz processor. Is included with the license
level 4 and 12V adapter. The RB750 series consists of 2, ie the RB750
and RB750G that support GbE (Gigabit Ethernet)-the rate of 1000 Mbit /
s.
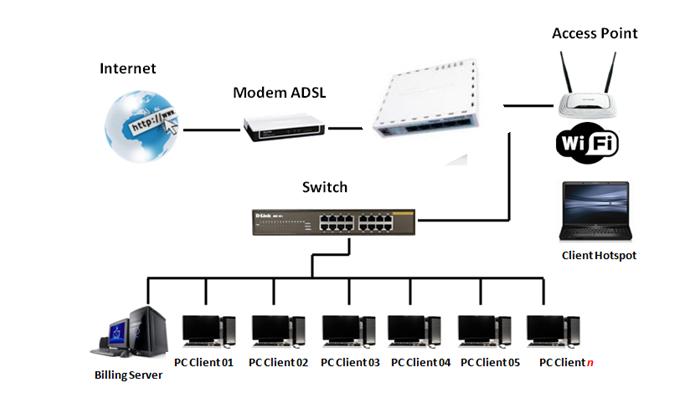 By
default MikroTik RB750 was directly we can use as gateway for internet
connection such asADSL internet connection with Speedy . Addition
RouterBoard as this gateway will cause increased one hop (jump) again
before the traffic in / out privileges internet, but it will not have
much effect on the network that we will use. Speedy Internet Connection
with MikroTik RB750From
a short manual that I get outside the box MikroTik RB750, RB750
Mikrotik turns to use it very easily, following step by step internet
connection with MikroTik RB750 as the gateway:
By
default MikroTik RB750 was directly we can use as gateway for internet
connection such asADSL internet connection with Speedy . Addition
RouterBoard as this gateway will cause increased one hop (jump) again
before the traffic in / out privileges internet, but it will not have
much effect on the network that we will use. Speedy Internet Connection
with MikroTik RB750From
a short manual that I get outside the box MikroTik RB750, RB750
Mikrotik turns to use it very easily, following step by step internet
connection with MikroTik RB750 as the gateway:

- Connect internet connection (cable UTP) from Speedy modem to Port 1 MikroTik RB750.
- To connect to a computer / client we can use Port 2,3,4 or 5, meaning a maximum of 4 pieces of the PC Client which can be connected directly.
- Further to the IP address settings for each PC Client we set the automatic. This is done for each connected client pc can get a dynamic IP address from the Router MikroTik.
- Make sure all connections are connected properly, can be done to check the following things:
- check whether it can be the ip of the router, open a command prompt type: ipconfig / all, should every computer will get an IP address in the range between 192.168.88.10/24 up 192.168.88.254/24.
- check whether it is connected to the Modem Speedy, type: ping 192.168.1.1 (the default address of the modem).
- check whether it is connected to the Internet, type: ping google.com
- After all goes as it should, it means we’ve been able to connect to the internet.
MikroTik RouterOS Firewall Basic
1. Chain & Action
Protecting the router – allowing only necessaryservices from reliable source addresses with agreeable load.
• To deny access to router to the router via Telnet (TCP port 23)
/ip firewall filter add chain=input protocol=tcp dst-port=23 action=drop
3. Chain Forward
Protecting the customers from viruses and protecting the Internet from the customers
Protecting Your Customer
• Block IP addreses called “bogons”:
add chain=forward src-address=0.0.0.0/8 action=drop
add chain=forward dst-address=0.0.0.0/8 action=drop
add chain=forward src-address=127.0.0.0/8 action=drop
add chain=forward dst-address=127.0.0.0/8 action=drop
add chain=forward src-address=224.0.0.0/3 action=drop
add chain=forward dst-address=224.0.0.0/3 action=drop
4. Condition: Connection State
Firewall address lists allow user to create lists of IP addresses grouped together. Firewall filter, mangle and NAT facilities can use address lists to match packets against them.
The address list records could be updated dynamically via the action=add-src-to-address-list or action=add-dst-to-address-list items found in NAT mangle and filter facilities.
The following example creates an address list of people thet are connecting to port 23 (telnet) on the router and drops all further traffic from them. Additionaly, the address list will contain one static entry of address=192.0.34.166/32 (www.example.com):
/ip firewall address-list add list=drop_traffic address=192.0.34.166/32
/ip firewall mangle add chain=prerouting protocol=tcp dst-port=23 action=add-src-to-address-list address-list=drop_traffic
/ip firewall filter add action=drop chain=input src-address-list=drop_traffic
6. NAT Type
As there are 2 IP addresses and ports in an IP packet header, there are 2 types of NAT .
1. which rewrites source IP address and/or port is called source NAT (src-nat)
Firewall NAT rules are organized in chains, There are two default chains :
8. NAT Action (6 specific action NAT)
- Firewall filter rules are organized in chains
- There are default and user-defined chains
- There are three default chains :
- input – processes packets sent to the router
- output – processes packets sent by the router
- forward – processes packets sent through the router
Protecting the router – allowing only necessaryservices from reliable source addresses with agreeable load.
• To deny access to router to the router via Telnet (TCP port 23)
/ip firewall filter add chain=input protocol=tcp dst-port=23 action=drop
3. Chain Forward
Protecting the customers from viruses and protecting the Internet from the customers
Protecting Your Customer
• Block IP addreses called “bogons”:
add chain=forward src-address=0.0.0.0/8 action=drop
add chain=forward dst-address=0.0.0.0/8 action=drop
add chain=forward src-address=127.0.0.0/8 action=drop
add chain=forward dst-address=127.0.0.0/8 action=drop
add chain=forward src-address=224.0.0.0/3 action=drop
add chain=forward dst-address=224.0.0.0/3 action=drop
4. Condition: Connection State
- Connection state is a status assigned to each packet by conntrack system:
- New – packet is opening a new connection
- Related – packet is also opening a new connection, but it is in some kind of relation to an already established connection
- Established – packet belongs to an already known connection
- Invalid – packet does not belong to any of the known connections
- Connection state ≠ TCP state
Firewall address lists allow user to create lists of IP addresses grouped together. Firewall filter, mangle and NAT facilities can use address lists to match packets against them.
The address list records could be updated dynamically via the action=add-src-to-address-list or action=add-dst-to-address-list items found in NAT mangle and filter facilities.
The following example creates an address list of people thet are connecting to port 23 (telnet) on the router and drops all further traffic from them. Additionaly, the address list will contain one static entry of address=192.0.34.166/32 (www.example.com):
/ip firewall address-list add list=drop_traffic address=192.0.34.166/32
/ip firewall mangle add chain=prerouting protocol=tcp dst-port=23 action=add-src-to-address-list address-list=drop_traffic
/ip firewall filter add action=drop chain=input src-address-list=drop_traffic
6. NAT Type
As there are 2 IP addresses and ports in an IP packet header, there are 2 types of NAT .
1. which rewrites source IP address and/or port is called source NAT (src-nat)
- performed on packet that are originated from natted network
- a NAT router replace the private source address of an IP packet with anew public IP Address as it travel trough the router.
- performed on packet that a destined to the natted network,
- it’s most commonly used to make ahost on private network to be accessible from internet
Firewall NAT rules are organized in chains, There are two default chains :
- dstnat – processes traffic sent to and through the router, before it divides in to “input” and “forward” chain of firewall filter.
- srcnat – processes traffic sent from and through the router, after it merges from “output” and “forward” chain of firewall filter.
8. NAT Action (6 specific action NAT)
- dst-nat and redirect
- src-nat and masquarade
- netmap
- same
- Action “src-nat” changes packet’s source address and/or port to specified address and/or Port
- This action can take place only in chain srcnat
- Typical application: hide specific LAN resources behind specific public IP address
- Action “masquerade” changes packet’s source address router’s address and specified port
- This action can take place only in chain srcnat
- Typical application: hide specific LAN resources behind one dynamic public IP address
- Action “dst-nat” changes packet’s destination address and port to specified address and port
- This action can take place only in chain dstnat
- Typical application: ensure access to local network services from public network
- Action “redirect” changes packet’s destination address to router’s address and specified port
- This action can take place only in chain dstnat
- Typical application: transparent proxying of network services (DNS,HTTP)
- Netmap – creates a static 1:1 mapping of one set of IP addresses to another one. Often used to distribute public IP addresses to hosts on private networks
- Same – gives a particular client the same source/destination IP address from the supplied range for any connection. Used for services that expect constant IP address for multiple connections from the same client
Welcome Page for PPPoE, DHCP, PPPTP Servers
1. ip firewall address-list you can put single ip aur pool for display your message
2. ip firewall nat i use my web server to load/display message.
/ip firewall filter
add action=jump chain=forward dst-port=80 jump-target=Reminder protocol=tcp \
src-address-list=Reminder
add action=add-src-to-address-list address-list=2_www address-list-timeout=1h \
chain=Reminder src-address-list=1_www
add action=return chain=Reminder src-address-list=2_www
add action=add-src-to-address-list address-list=1_www address-list-timeout=5s \
chain=Reminder
Note:
Firewall filter rules should be on top
/ip firewall nat
add action=dst-nat chain=dstnat comment=”Redirect to Message Server” \
dst-port=80 protocol=tcp src-address-list=1_www to-addresses=192.168.1.6 \
to-ports=80
Note:
Firewall Rule should be on top
/ip firewall address-list
add address=10.10.50.2-10.10.50.10 comment=\
“Reminder to Customer For Payment/Message” list=Reminder
Note:
Add address as per your ip pool.
2. ip firewall nat i use my web server to load/display message.
/ip firewall filter
add action=jump chain=forward dst-port=80 jump-target=Reminder protocol=tcp \
src-address-list=Reminder
add action=add-src-to-address-list address-list=2_www address-list-timeout=1h \
chain=Reminder src-address-list=1_www
add action=return chain=Reminder src-address-list=2_www
add action=add-src-to-address-list address-list=1_www address-list-timeout=5s \
chain=Reminder
Note:
Firewall filter rules should be on top
/ip firewall nat
add action=dst-nat chain=dstnat comment=”Redirect to Message Server” \
dst-port=80 protocol=tcp src-address-list=1_www to-addresses=192.168.1.6 \
to-ports=80
Note:
Firewall Rule should be on top
/ip firewall address-list
add address=10.10.50.2-10.10.50.10 comment=\
“Reminder to Customer For Payment/Message” list=Reminder
Note:
Add address as per your ip pool.
3 Wan Unequal Load balancing PCC Method
# Interface name for Local = Local
# Interface name for wan1 = WAN1
# Interface name for wan2 = WAN2
# Interface name for wan3 = WAN3
#
#
#
# Wan1 is double in speed
#
/ip address
add address=192.168.0.1/24 network=192.168.0.0 broadcast=192.168.0.255 interface=Local
add address=192.168.1.5/24 network=192.168.1.0 broadcast=192.168.1.255 interface=WAN1
add address=192.168.2.5/24 network=192.168.2.0 broadcast=192.168.2.255 interface=WAN2
add address=192.168.3.5/24 network=192.168.3.0 broadcast=192.168.3.255 interface=WAN3
/ip dns set allow-remote-requests=yes cache-max-ttl=1w cache-size=5000KiB max-udp-packet-size=4096 servers=221.132.112.8,8.8.8.8
/ip firewall mangle
add chain=input in-interface=WAN1 action=mark-connection new-connection-mark=WAN1_conn
add chain=input in-interface=WAN2 action=mark-connection new-connection-mark=WAN2_conn
add chain=input in-interface=WAN3 action=mark-connection new-connection-mark=WAN3_conn
add chain=output connection-mark=WAN1_conn action=mark-routing new-routing-mark=to_WAN1
add chain=output connection-mark=WAN2_conn action=mark-routing new-routing-mark=to_WAN2
add chain=output connection-mark=WAN3_conn action=mark-routing new-routing-mark=to_WAN3
add chain=prerouting dst-address=192.168.1.0/24 action=accept in-interface=Local
add chain=prerouting dst-address=192.168.2.0/24 action=accept in-interface=Local
add chain=prerouting dst-address=192.168.3.0/24 action=accept in-interface=Local
add chain=prerouting dst-address-type=!local in-interface=Local per-connection-classifier=both-addresses-and-ports:4/0 action=mark-connection new-connection-mark=WAN1_conn passthrough=yes
add chain=prerouting dst-address-type=!local in-interface=Local per-connection-classifier=both-addresses-and-ports:4/1 action=mark-connection new-connection-mark=WAN1_conn passthrough=yes
add chain=prerouting dst-address-type=!local in-interface=Local per-connection-classifier=both-addresses-and-ports:4/2 action=mark-connection new-connection-mark=WAN2_conn passthrough=yes
add chain=prerouting dst-address-type=!local in-interface=Local per-connection-classifier=both-addresses-and-ports:4/3 action=mark-connection new-connection-mark=WAN3_conn passthrough=yes
add chain=prerouting connection-mark=WAN1_conn in-interface=Local action=mark-routing new-routing-mark=to_WAN1
add chain=prerouting connection-mark=WAN2_conn in-interface=Local action=mark-routing new-routing-mark=to_WAN2
add chain=prerouting connection-mark=WAN3_conn in-interface=Local action=mark-routing new-routing-mark=to_WAN3
/ip route
add dst-address=0.0.0.0/0 gateway=192.168.1.1 routing-mark=to_WAN1 check-gateway=ping
add dst-address=0.0.0.0/0 gateway=192.168.2.1 routing-mark=to_WAN2 check-gateway=ping
add dst-address=0.0.0.0/0 gateway=192.168.3.1 routing-mark=to_WAN3 check-gateway=ping
add dst-address=0.0.0.0/0 gateway=192.168.1.1 distance=1 check-gateway=ping
add dst-address=0.0.0.0/0 gateway=192.168.2.1 distance=2 check-gateway=ping
add dst-address=0.0.0.0/0 gateway=192.168.3.1 distance=3 check-gateway=ping
/ip firewall nat
add chain=srcnat out-interface=WAN1 action=masquerade
add chain=srcnat out-interface=WAN2 action=masquerade
add chain=srcnat out-interface=WAN3 action=masquerade
# Interface name for wan1 = WAN1
# Interface name for wan2 = WAN2
# Interface name for wan3 = WAN3
#
#
#
# Wan1 is double in speed
#
/ip address
add address=192.168.0.1/24 network=192.168.0.0 broadcast=192.168.0.255 interface=Local
add address=192.168.1.5/24 network=192.168.1.0 broadcast=192.168.1.255 interface=WAN1
add address=192.168.2.5/24 network=192.168.2.0 broadcast=192.168.2.255 interface=WAN2
add address=192.168.3.5/24 network=192.168.3.0 broadcast=192.168.3.255 interface=WAN3
/ip dns set allow-remote-requests=yes cache-max-ttl=1w cache-size=5000KiB max-udp-packet-size=4096 servers=221.132.112.8,8.8.8.8
/ip firewall mangle
add chain=input in-interface=WAN1 action=mark-connection new-connection-mark=WAN1_conn
add chain=input in-interface=WAN2 action=mark-connection new-connection-mark=WAN2_conn
add chain=input in-interface=WAN3 action=mark-connection new-connection-mark=WAN3_conn
add chain=output connection-mark=WAN1_conn action=mark-routing new-routing-mark=to_WAN1
add chain=output connection-mark=WAN2_conn action=mark-routing new-routing-mark=to_WAN2
add chain=output connection-mark=WAN3_conn action=mark-routing new-routing-mark=to_WAN3
add chain=prerouting dst-address=192.168.1.0/24 action=accept in-interface=Local
add chain=prerouting dst-address=192.168.2.0/24 action=accept in-interface=Local
add chain=prerouting dst-address=192.168.3.0/24 action=accept in-interface=Local
add chain=prerouting dst-address-type=!local in-interface=Local per-connection-classifier=both-addresses-and-ports:4/0 action=mark-connection new-connection-mark=WAN1_conn passthrough=yes
add chain=prerouting dst-address-type=!local in-interface=Local per-connection-classifier=both-addresses-and-ports:4/1 action=mark-connection new-connection-mark=WAN1_conn passthrough=yes
add chain=prerouting dst-address-type=!local in-interface=Local per-connection-classifier=both-addresses-and-ports:4/2 action=mark-connection new-connection-mark=WAN2_conn passthrough=yes
add chain=prerouting dst-address-type=!local in-interface=Local per-connection-classifier=both-addresses-and-ports:4/3 action=mark-connection new-connection-mark=WAN3_conn passthrough=yes
add chain=prerouting connection-mark=WAN1_conn in-interface=Local action=mark-routing new-routing-mark=to_WAN1
add chain=prerouting connection-mark=WAN2_conn in-interface=Local action=mark-routing new-routing-mark=to_WAN2
add chain=prerouting connection-mark=WAN3_conn in-interface=Local action=mark-routing new-routing-mark=to_WAN3
/ip route
add dst-address=0.0.0.0/0 gateway=192.168.1.1 routing-mark=to_WAN1 check-gateway=ping
add dst-address=0.0.0.0/0 gateway=192.168.2.1 routing-mark=to_WAN2 check-gateway=ping
add dst-address=0.0.0.0/0 gateway=192.168.3.1 routing-mark=to_WAN3 check-gateway=ping
add dst-address=0.0.0.0/0 gateway=192.168.1.1 distance=1 check-gateway=ping
add dst-address=0.0.0.0/0 gateway=192.168.2.1 distance=2 check-gateway=ping
add dst-address=0.0.0.0/0 gateway=192.168.3.1 distance=3 check-gateway=ping
/ip firewall nat
add chain=srcnat out-interface=WAN1 action=masquerade
add chain=srcnat out-interface=WAN2 action=masquerade
add chain=srcnat out-interface=WAN3 action=masquerade

This comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeletenice info
ReplyDelete